Configuring an Azure function behind a NAT gateway to restrict outgoing IP addresses
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Use of Azure NAT
- Create an Azure virtual network using function subnets
- Create a premium Azure Function app
- Create an HTTP trigger function to display the outgoing IP
- Using Vnet Integration in Azure Functions
- Create a NAT gateway and associate it with an Azure virtual network subnet
- Check the Azure Function NAT configuration
- Conclusion
Introduction
Azure Virtual Network Address Translation is a fully managed and resilient PaaS offering from Azure that simplifies outbound connectivity to virtual networks. You can define a virtual network egress connection to one or more subnets of a virtual network using a single public IP or a public IP prefix resource, or a combination of both. Once configured, traffic is routed through the NAT gateway without a custom route table.
Use of Azure NAT
If your application requires a static IP address or range of IP addresses when sending traffic over the Internet or to a remote endpoint, Azure NAT is an easy solution to meet these requirements. Similar functionality can be achieved using a load balancer but using a NAT gateway makes it easy to configure and manage traffic flows without much effort. NAT uses Port NAT and is the recommended solution when deploying solutions in Azure.
In this article, you'll understand how to configure an Azure function behind a NAT gateway to restrict outgoing IP addresses.
Create an Azure virtual network using function subnets
An Azure virtual network is the building block for secure communication between Azure resources, the Internet, and an on-premises network. It provides features such as network traffic filtering, routing, DDoS protection, and integration with other Azure services.
- In the Azure portal, enter
virtual networksin the top search box and click Virtual Networks under Services.
- To create a new virtual network resource, click the
Create Virtual Networkbutton in the middle of the window.
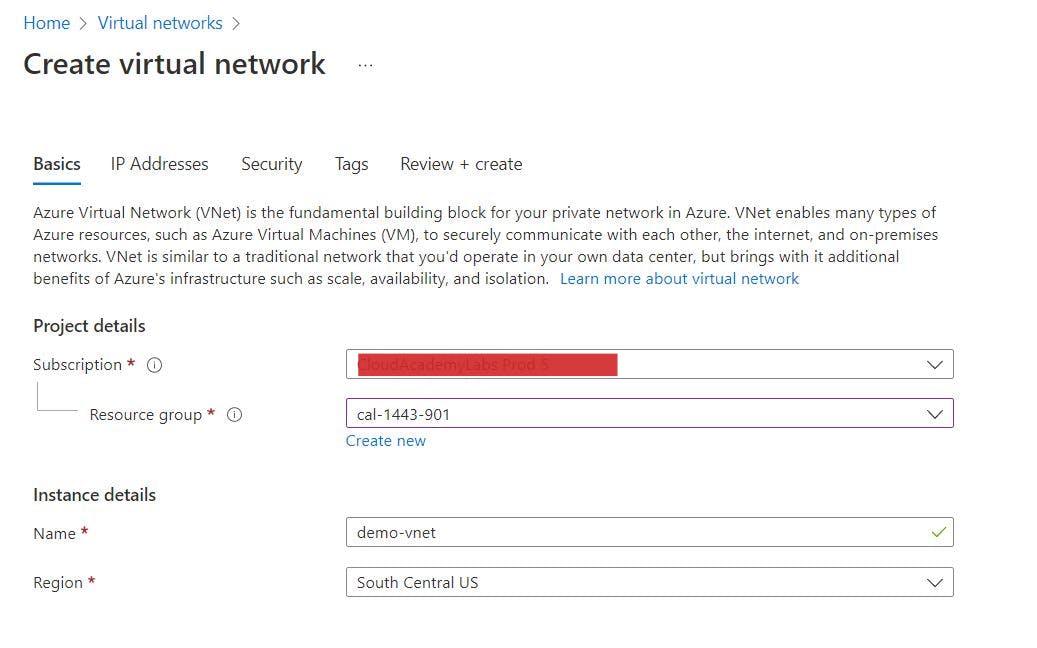
- In the Create virtual network box that appears, enter the following values in the Default tab.
- Click Next: View the network IP addresses and IPv4 address space.
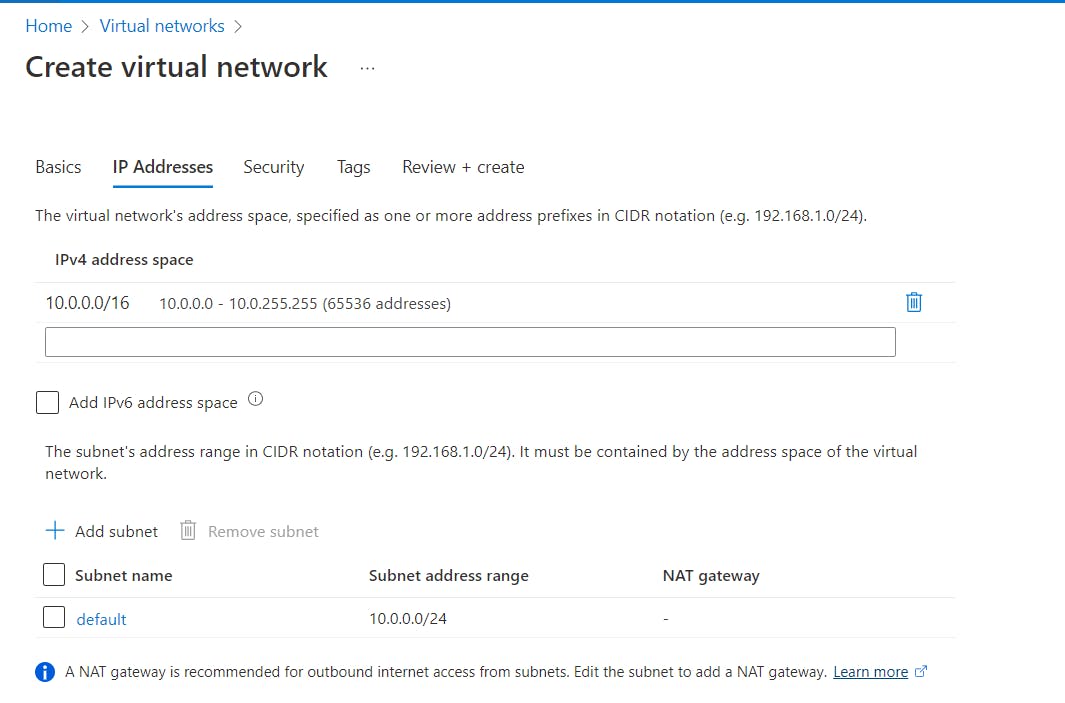
- On the same page, click
+ Add Subnet, click Add Subnet in the pop-up window, enter the following information, and then clickAdd.
Subnet Name: function-subnet Subnet address range: 10.0.1.0/24
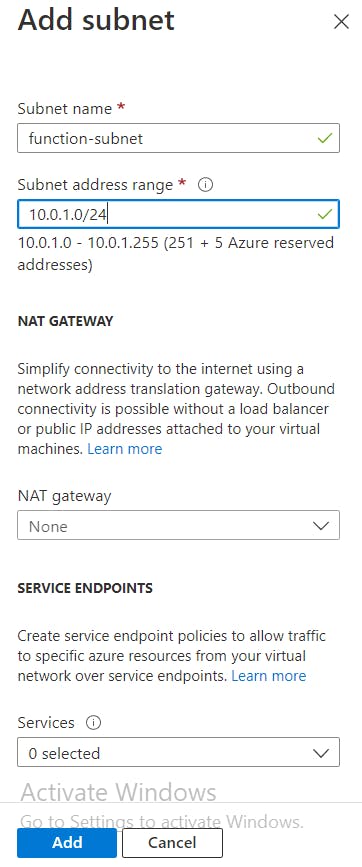
You will use this private subnet to configure a NAT gateway to control traffic flow to the Azure Function.
- Click Next: Security and review the configuration.
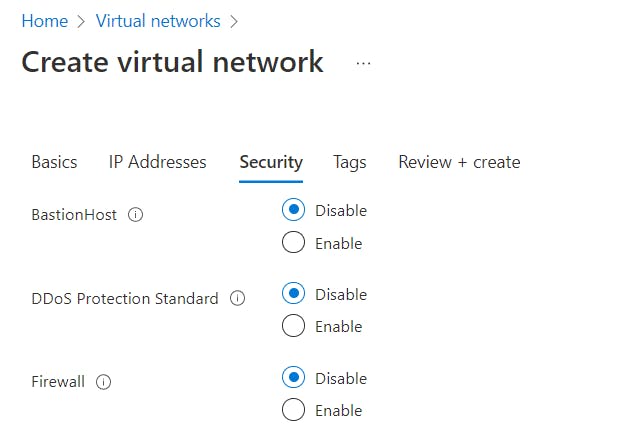
- Click
Review + Createto review the settings, then clickCreateto begin creating your virtual network resource.
Create a premium Azure Function app
Azure Functions is a serverless computing service in Microsoft Azure. You can deploy your code using Azure Functions without worrying about the servers your code will run on. Azure features three basic hosting services, including consumer plans, premium plans, and dedicated plans. All three plans come with unique offerings and limitations, including scalability, security, network connectivity, and support for custom images.
- In the Azure portal, enter
Function Appin the top search box and selectFunction Appunder Services.
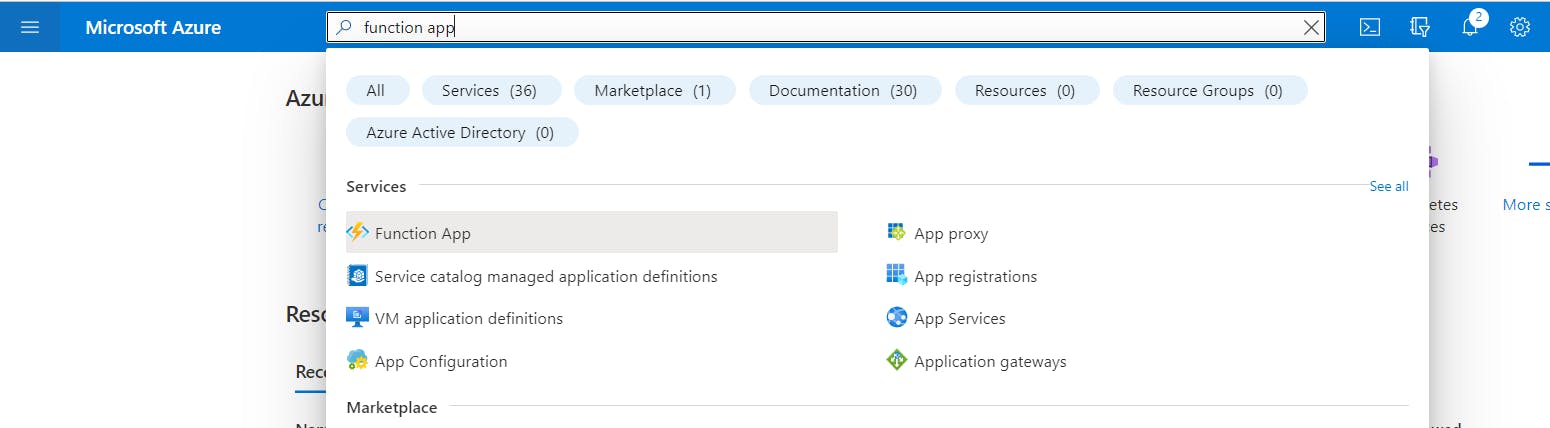
- Click
Create a function appin the center of the screen and enter the following values in the Basics tab of the Create Function App window.
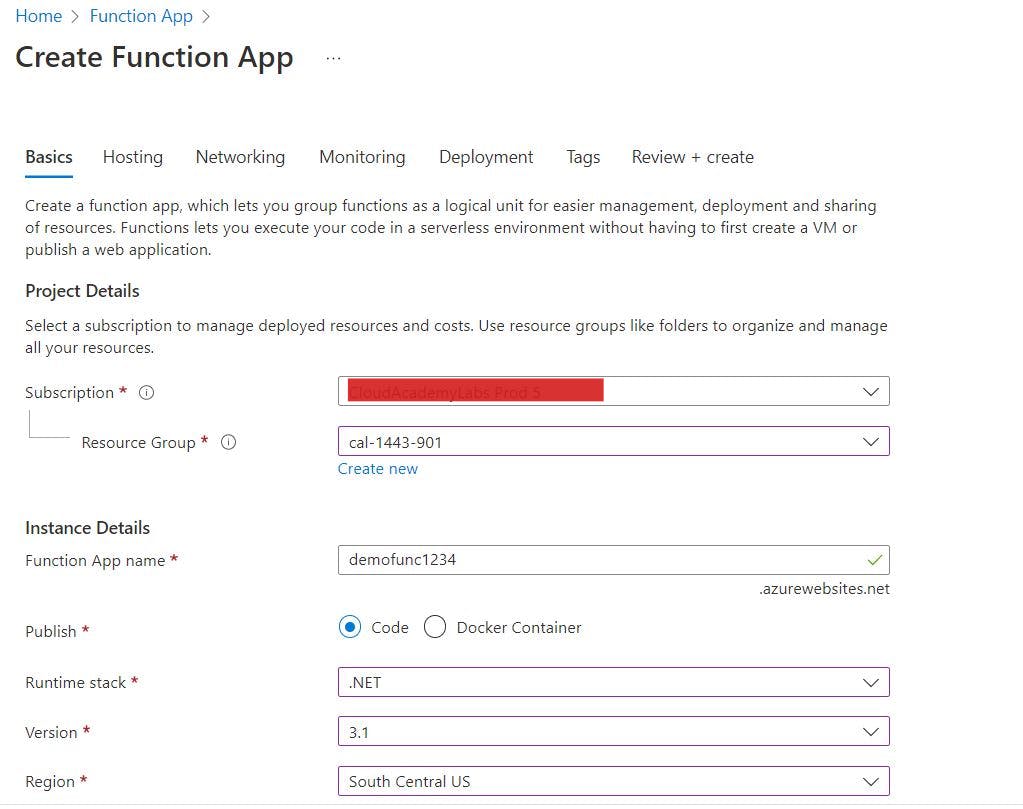
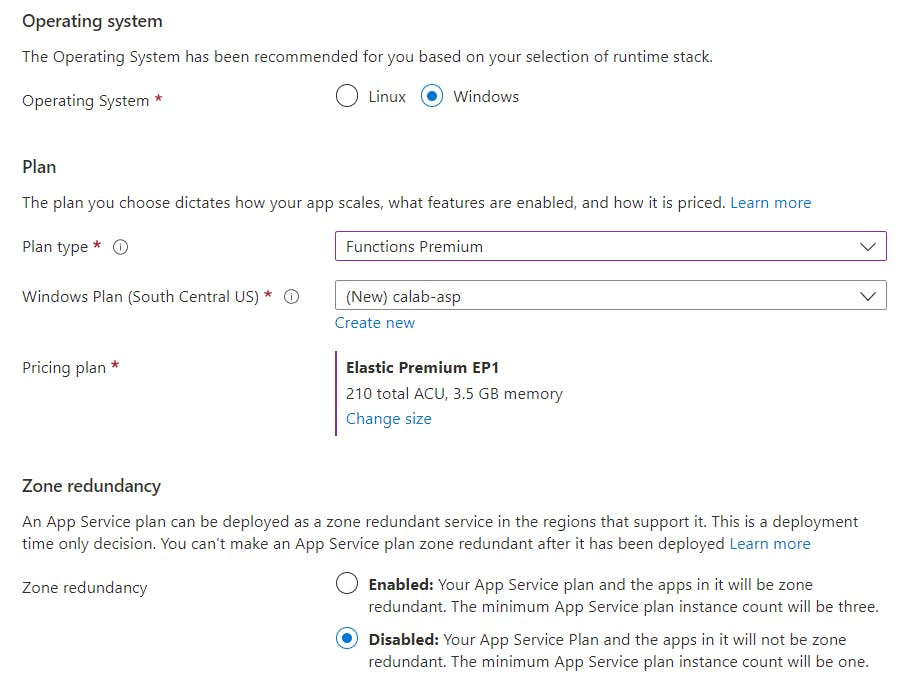
Click on the
Monitoringtab and make sure it is set to No.Click the
Review + Createtab and click theCreate.
Create an HTTP trigger function to display the outgoing IP
There are several ways to create and deploy Azure Functions. In production, you can set up a deployment mechanism that allows Azure Functions to pull the latest version of your code from your version control system. Function apps provide different types of functions, including HTTP triggers, Timer triggers, Cosmos DB triggers, Blob storage triggers and Queued storage triggers.
- In the top search bar of the Azure portal, search for the function app which was created earlier.
- To see your
Outbound IP addressesandAdditional Outbound IP Addresses, click thePropertiesbutton under Settings in the left panel menu.
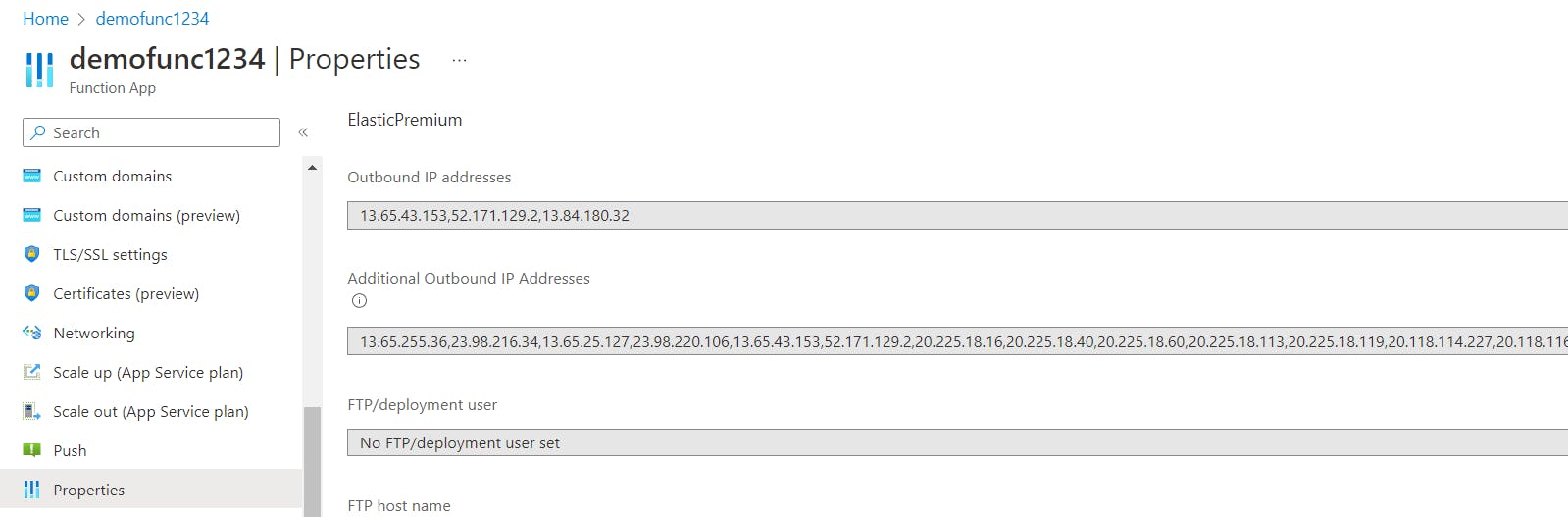
The IP addresses listed here are used by the platform as the source IP address when sending HTTP requests or feature-generated traffic.
- Select Functions from the left panel menu and click
+ Create.
- Select the
HTTP triggerfrom the Template to use.
- Enter
OutboundIPin the New function name field. When you're done, clickCreate.
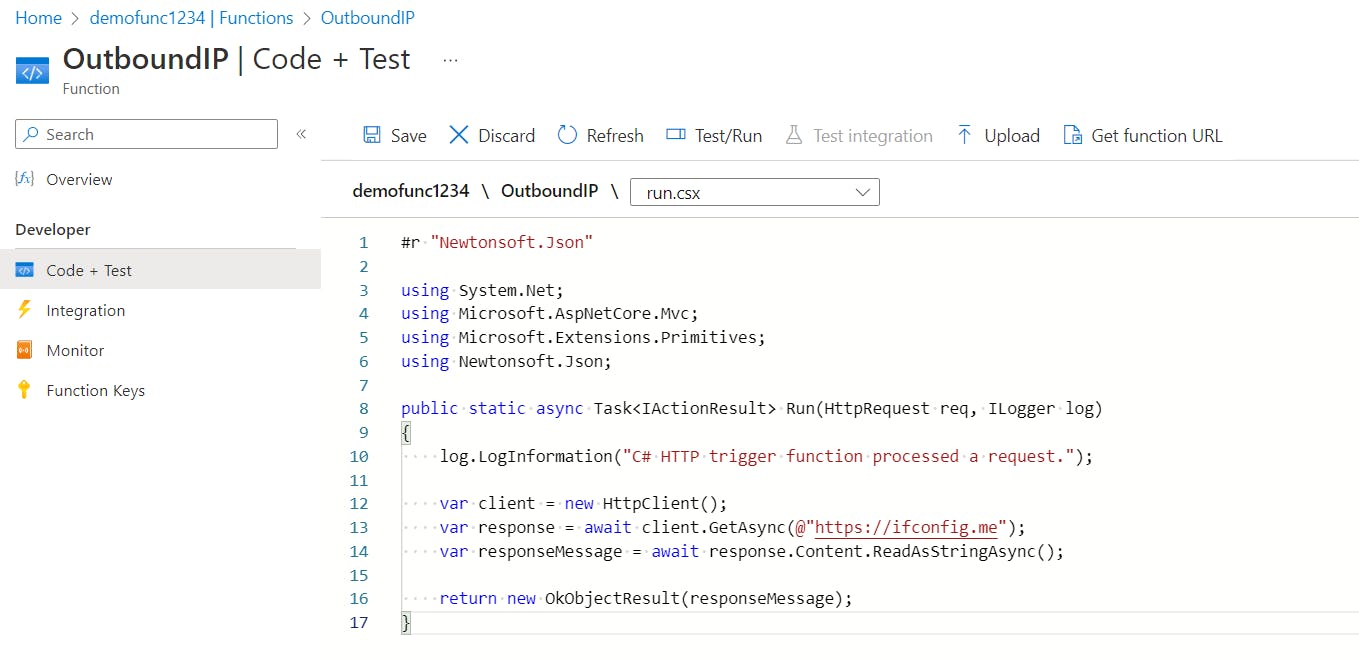
- Click
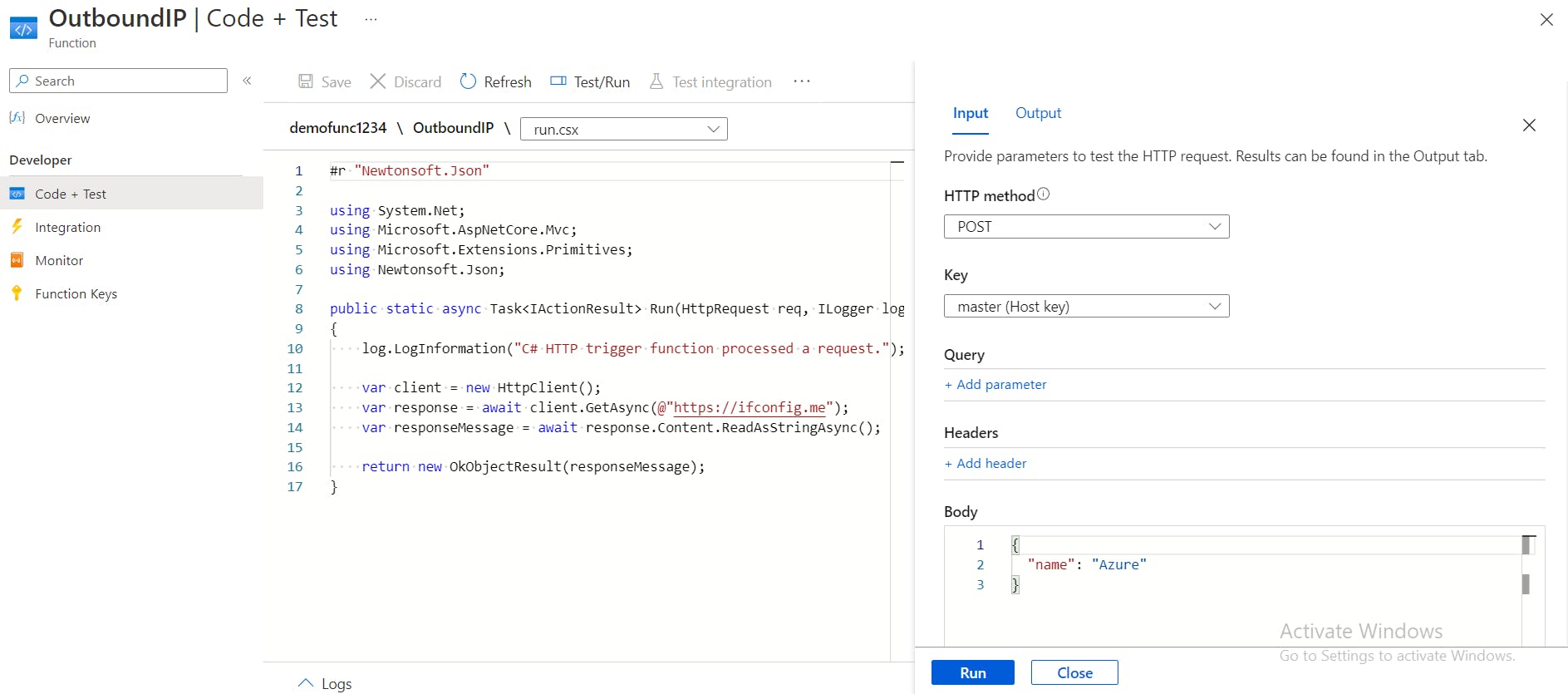
Code + Testfrom the left menu options and replace the editor code with the following code snippet.
#r "Newtonsoft.Json"
using System.Net;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Primitives;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
public static async Task<IActionResult> Run(HttpRequest req, ILogger log)
{
log.LogInformation("C# HTTP trigger function processed a request.");
var client = new HttpClient();
var response = await client.GetAsync(@"https://ifconfig.me");
var responseMessage = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
return new OkObjectResult(responseMessage);
}
The function above makes an HTTP request to get the public IP address of the network it uses to connect to the Internet. The response is then captured and displayed as part of the result.
- After changing the code, click
Save. ClickTest/Runand then clickRunto trigger the function app and leave thebodycontent as default.
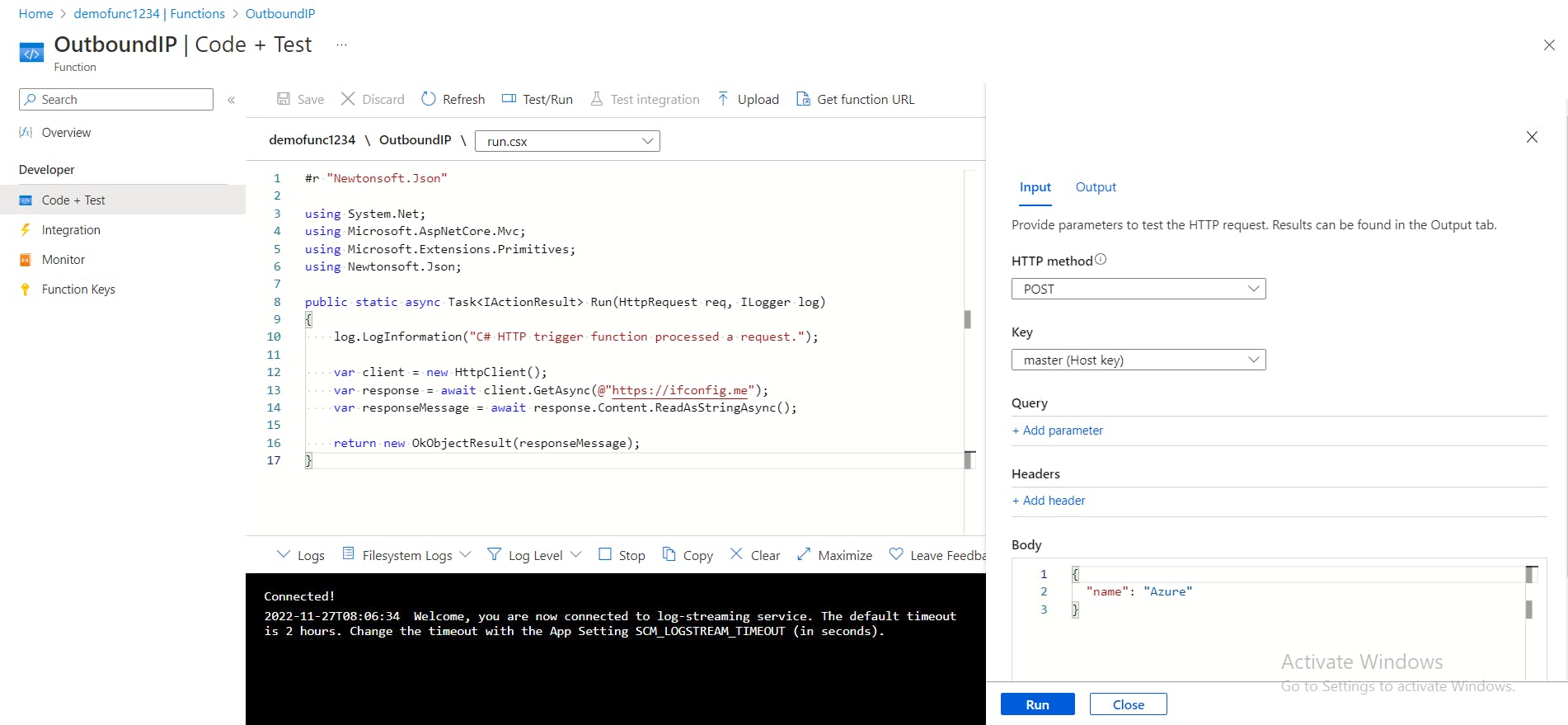
OUTPUT WINDOW
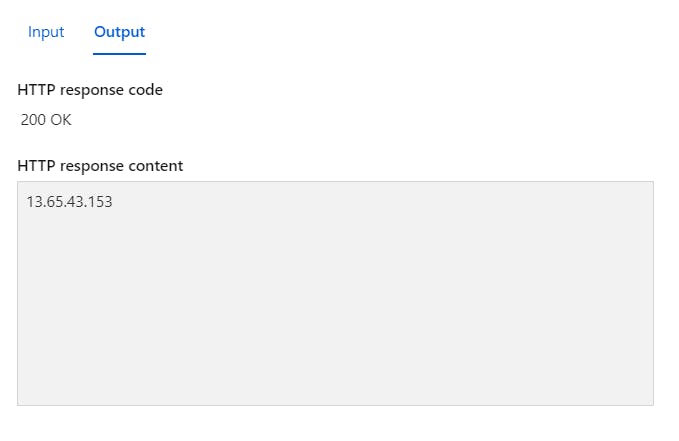
You should see an output that shows the outgoing IP address that the function application is using to communicate with the remote endpoint.
Using Vnet Integration in Azure Functions
You connect your function app to a virtual network subnet and test the function to ensure that the egress IP address of your function application is the same as the public IP address associated with your NAT gateway.
- Return to the Azure Function App resource. Under
Settingsin the left menu options, selectNetworkingand clickVirtual Network Integration.
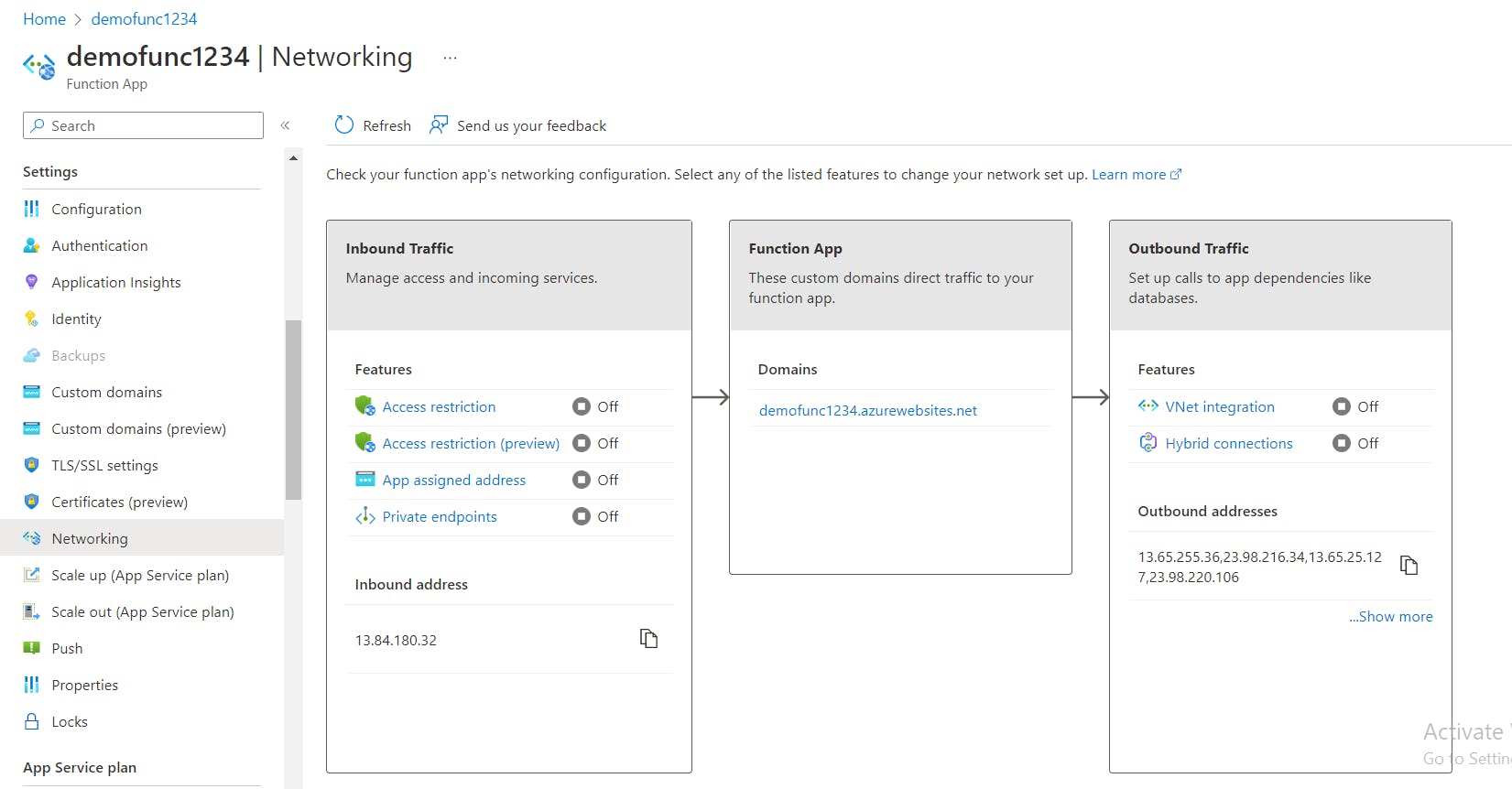
- Click the
+ Add virtual networkbutton and select thedemo-vnetvirtual network from theFunction-Subnetdrop-down list.
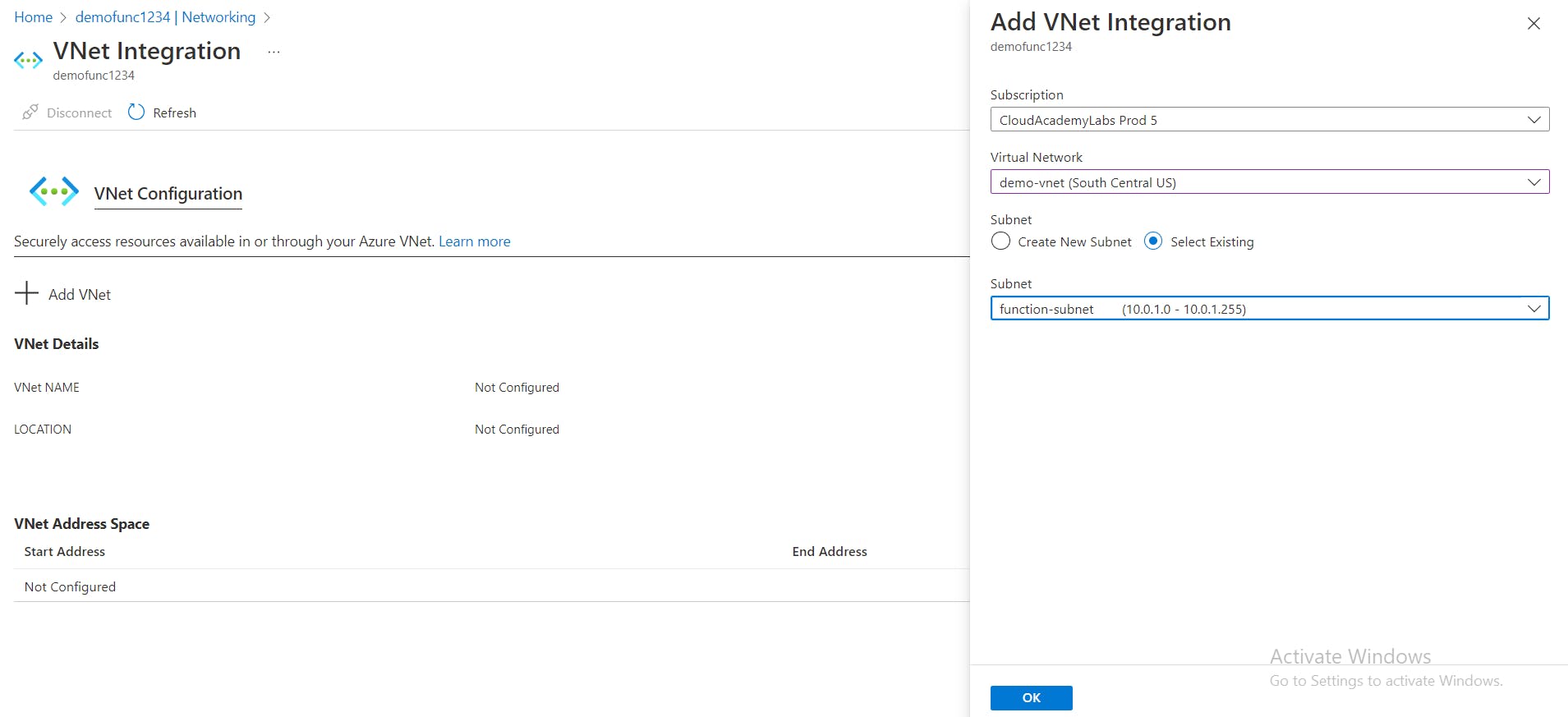
- Click
OKand wait for the deployment to complete.
- Once the connection is established, you will see the virtual network configuration listed on the Virtual Network Integration page.
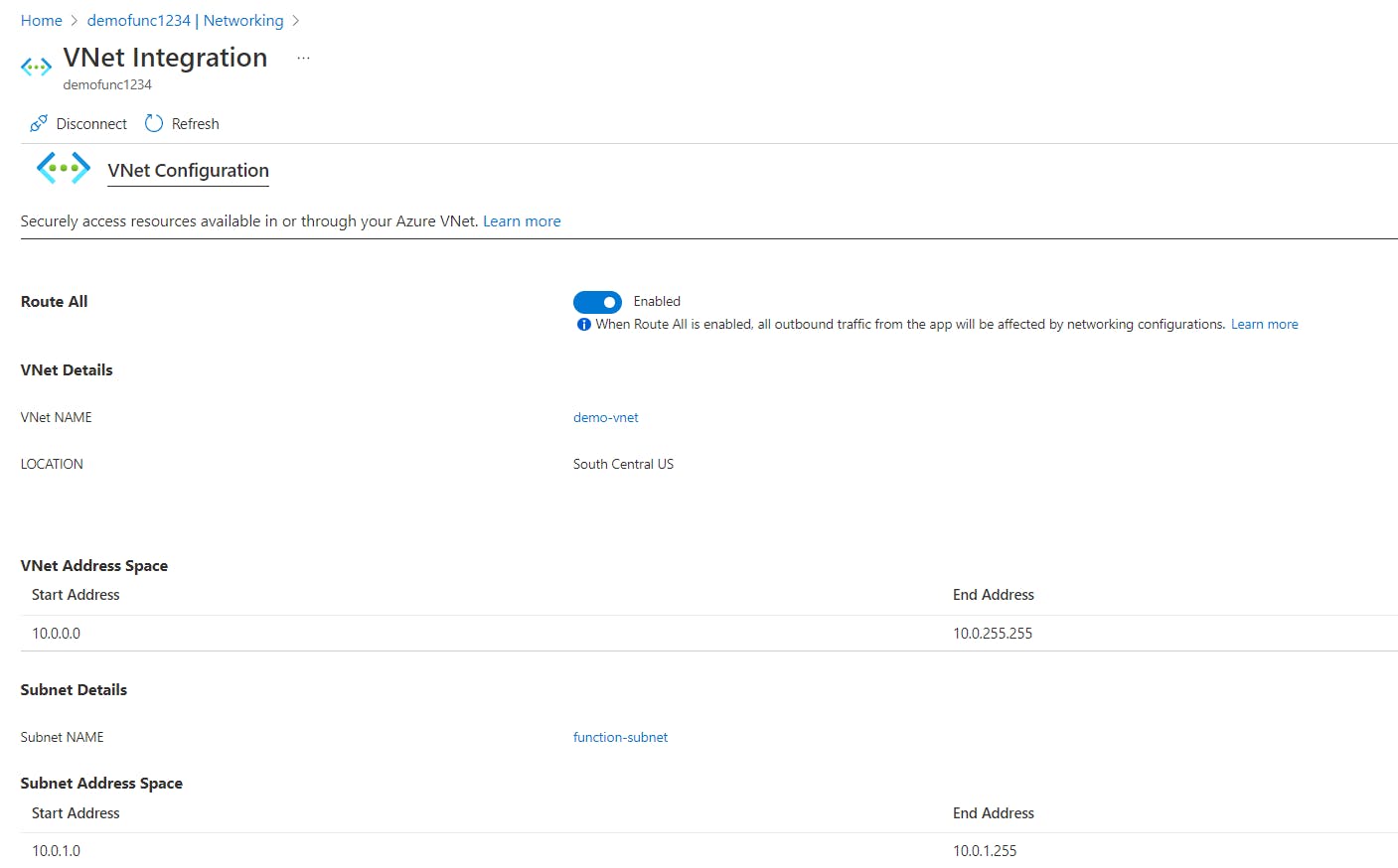
- Return to the Function app, select
ConfigurationunderSettingsfrom the left menu, and click+ New Application Setting.
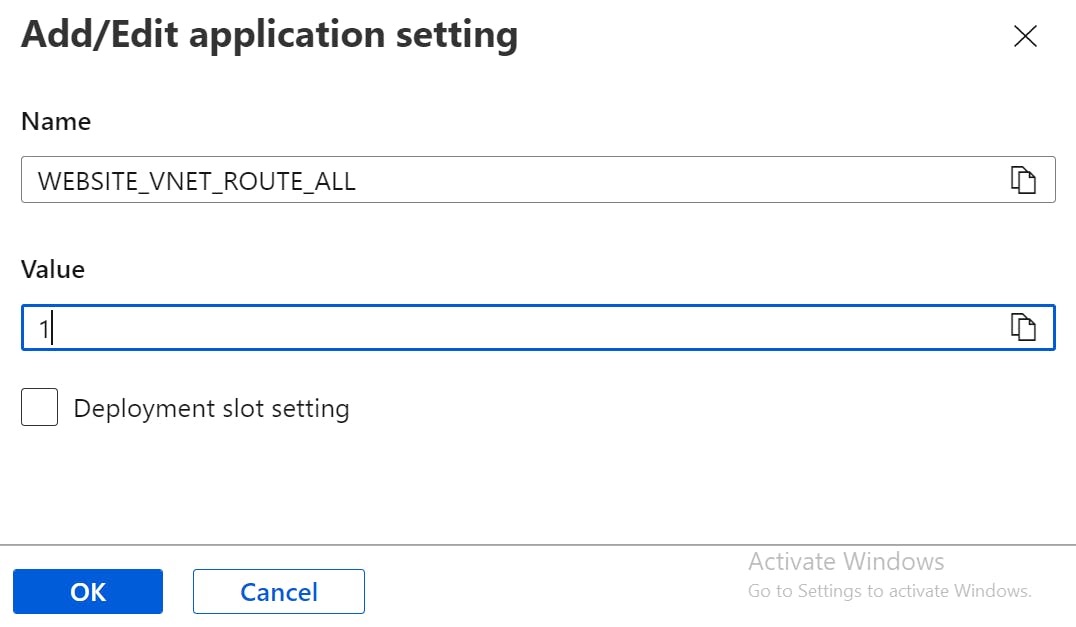
- Enter the following information for Name and Value and click OK.
Name: WEBSITE_VNET_ROUTE_ALL Value: 1
By default, this feature directs RFC1918 traffic to the virtual network only if the application is configured with virtual network integration. This means that by default it only points to the private IP address space and not to public IP addresses. The application settings configured above are required to redirect all outgoing traffic to the virtual network from the application.
- On the Setup page, click
Saveto finish configuring the app settings.
Create a NAT gateway and associate it with an Azure virtual network subnet
- Enter the
Public IPin the upper search window of the Azure portal and select the public IP address for the service.
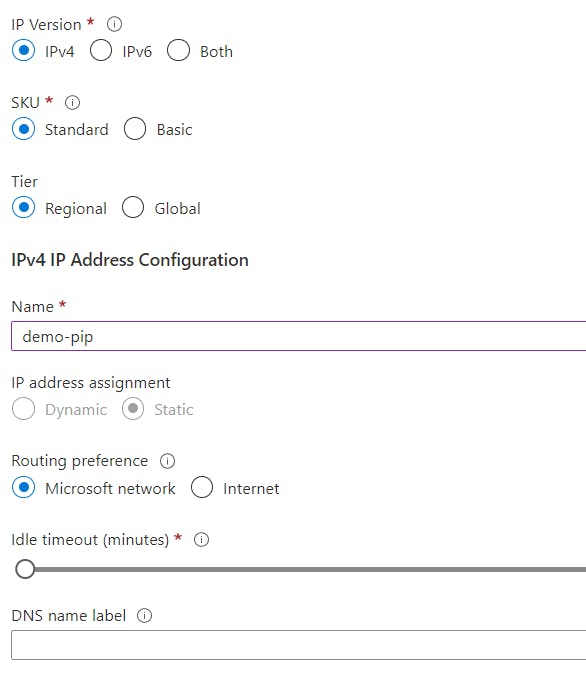
- In the middle of the screen, click on the Create Public IP address, use the following information from the Pop-Up window and click
Create.
- In the Azure portal search box, find
NAT Gatewayand selectNAT Gatewayunder the service.
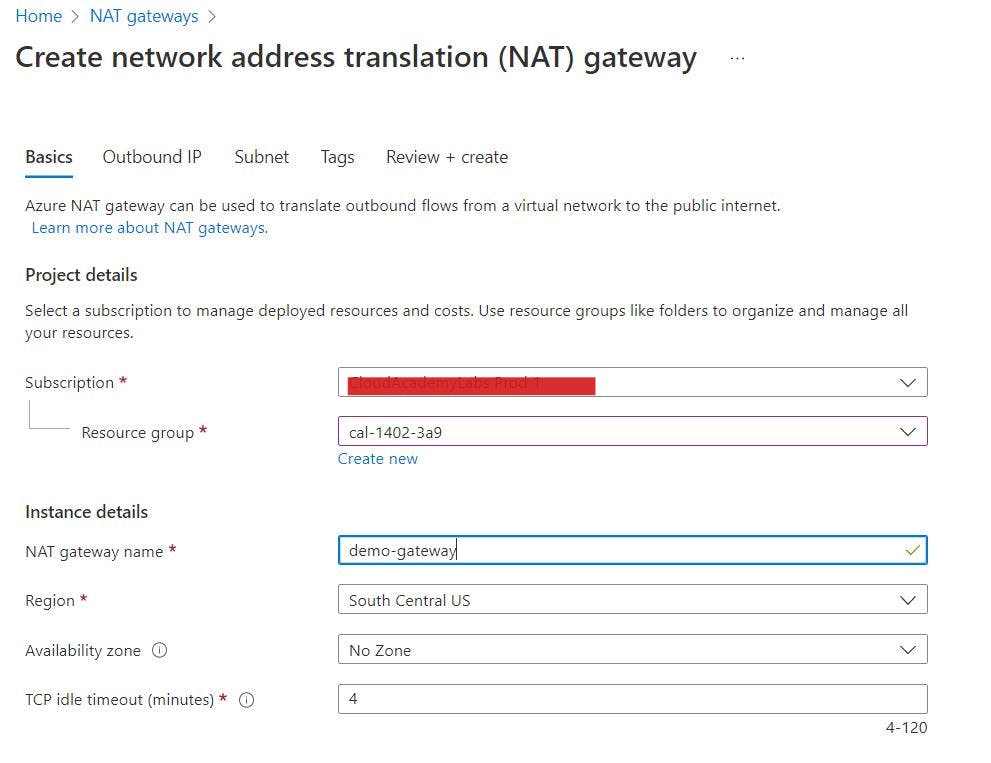
- Click the
Create NAT Gatewaybutton and enter the following information.
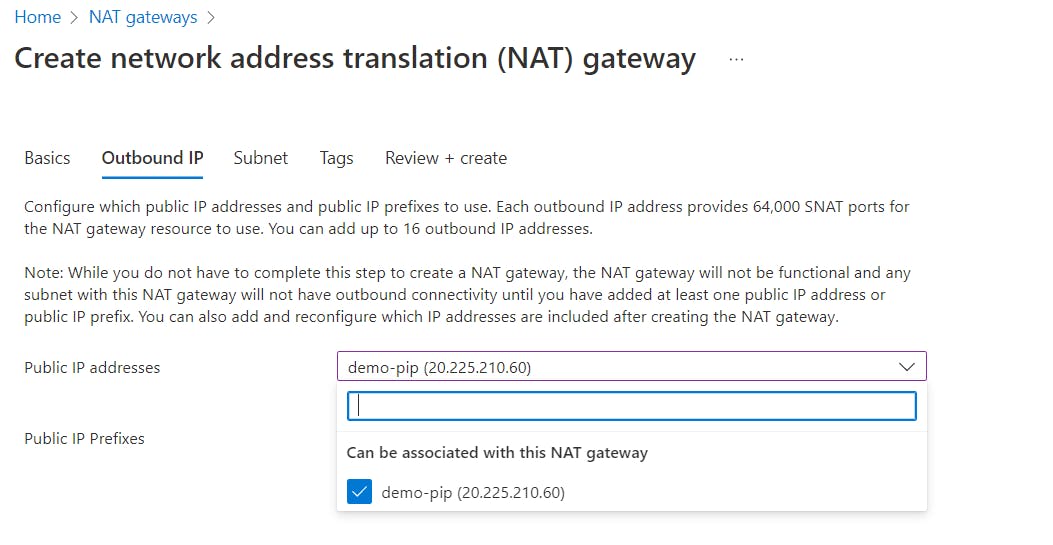
For now, click
Review + CreateandCreateto finish creating the resource.Under Settings on the left menu, click Subnets and select the following options for subnet settings:
Virtual Network: demo-vnet Subnet Name: function-subnet
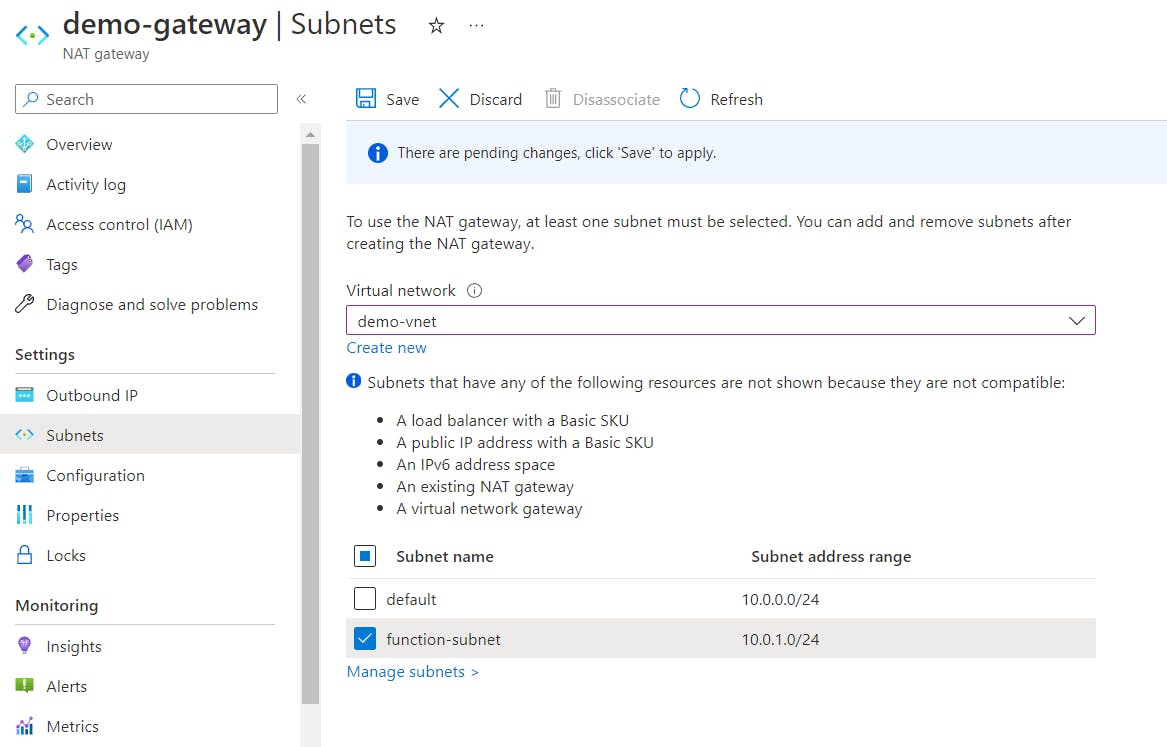
- When you're done, click
Save.
Check the Azure Function NAT configuration
- Go to the Azure Function resource under Function Options and click on the
OutboundIPfunction you created earlier.
- Click
Code + Test->Test/RunandRunto trigger the function.
- Check the output of the function.
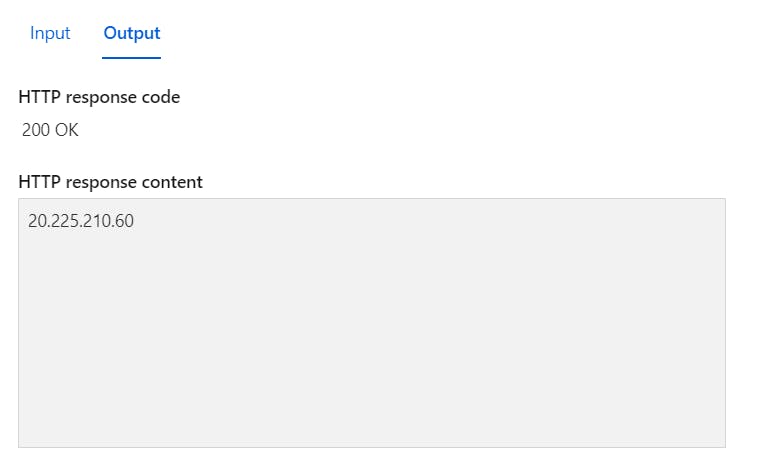
The IP addresses listed here correspond to public IP addresses configured as NAT gateways.
Navigate to the NAT Gateway resource under your account and click the Outbound IP.
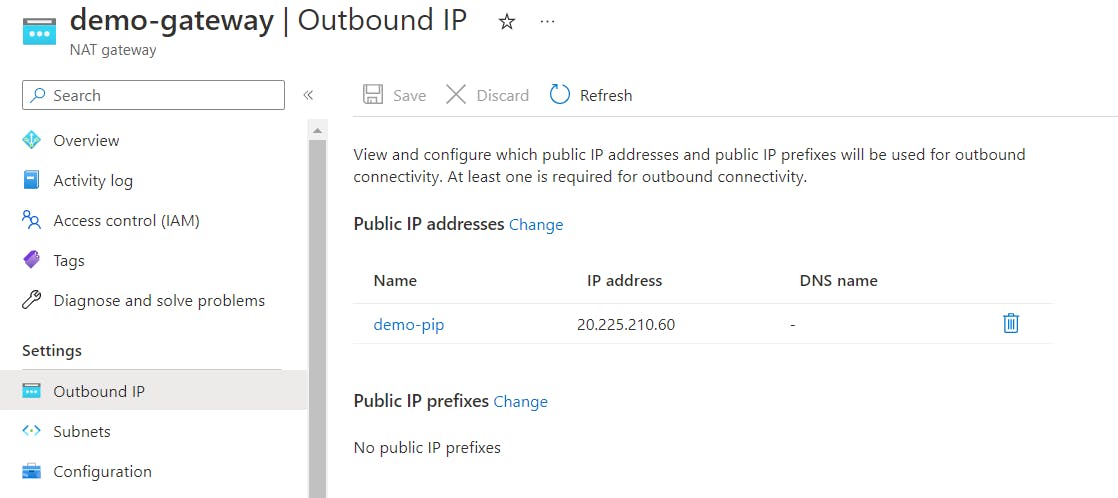
Conclusion
The IP addresses listed here match the output of the function, confirming that your Azure function has been configured with a NAT gateway and that all traffic now flows through the NAT gateway using the assigned public IP address and egress IP address.
Gratitude for perusing my article till the end. I hope you realized something unique today. If you enjoyed this article then please share it with your buddies and if you have suggestions or thoughts to share with me then please write in the comment box.
