Getting Started with AWS Config Rules and Remediation
Assess, audit, and evaluate configurations of your resources
Introduction to AWS Config

AWS Config provides a detailed view of the configuration of AWS resources in your AWS account. This includes how resources are related to each other and how resources have been organized in the past, so you can see how their configurations and relationships change over time.
Features
Resource management
Rules and conformance packs
Aggregators
Advanced queries
How AWS Config Works
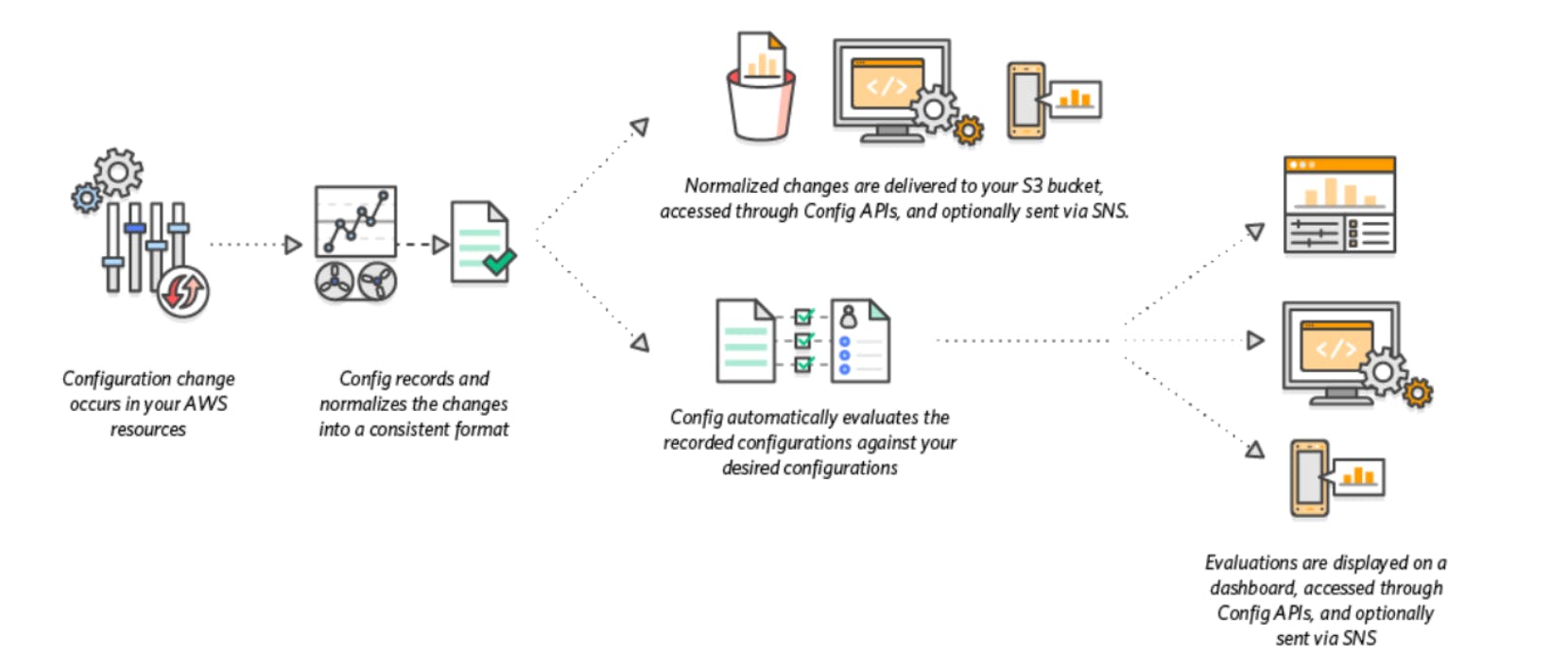
- When you enable AWS Config, it first identifies the supported AWS resources in your account and creates a configuration item for each resource.
- AWS Config also creates a configuration item when the resource configuration changes and keeps a historical record of the resource configuration item after the configuration author runs.
- By default, AWS Config creates a configuration item for each supported resource in a region.
- If you don't want AWS Config to create configuration items for all supported resources, you can specify the types of resources you want to track.
AWS Config tracks all resource changes by calling the Describe or List API calls for each resource in your account. The service uses the same API call to retrieve configuration details for all related resources.
For example,
If you delete an egress rule from a VPC security group, AWS Config makes an API describe call on the security group.
AWS Config then makes an API call to describe all instances associated with the security group. Updated configurations for security groups (resources) and each instance (related resources) are recorded as configuration items and delivered to the Amazon Simple Storage Service folder in the configuration flow.
AWS Config also tracks configuration changes not implemented in the API. AWS Config periodically checks the resource configuration and creates configuration items for changed configurations.
AWS Config rules
If you use AWS Config rules, AWS Config continuously evaluates the configuration of your AWS resources for the desired settings. Depending on the rule, AWS Config evaluates resources periodically or in response to configuration changes.
Each rule is associated with an AWS Lambda function that contains the rule's evaluation logic. When AWS Config evaluates a resource, it invokes the rule's AWS Lambda function. This function returns the match status of the evaluated resource.
If a resource violates the conditions of a rule, AWS Config marks the resource and the rule as non-compliant. When the compliance status of resource changes, AWS Config sends a notification to an Amazon SNS topic.
Kindly watch the below video to know more about AWS Config.
Compliance management
AWS Config is a service that allows you to view, monitor, and evaluate the configuration of your AWS resources. Config continuously monitors and logs AWS source configurations, which can automate the evaluation of logged configurations against desired configurations.
Scenario
Use AWS Config to determine which elastic network interfaces or ENIs are not attached to resources in your environment, and then use System Manager to restore resources marked as non-compliant.
- AWS Config allows you to define rules for evaluating the provisioning and configuration of AWS resources. These rules can be provided with bundled compliance remediation actions that can be implemented at the individual account or organization level.
- Initial configuration or configuration changes that deviate from the rules automatically trigger Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) notifications and Amazon CloudWatch events so you can stay informed.
Before you can start using the configuration, you must enable the configuration recording and configure a delivery channel.
Kindly watch the below video to get started with AWS Config rules and remediation.
Conclusion
In this article, you created a number of unattached elastic IP addresses and added an AWS configuration. You then implemented a rule to check for unattached EIPs and used Systems Manager Automation runbooks to fix the non-compliant resources.
Gratitude for perusing my article till the end. I hope you realized something unique today. If you enjoyed this article then please share it with your buddies and if you have suggestions or thoughts to share with me then please write in the comment box.
