Table of contents
- Introduction
- What will happen if time is not set correctly?
- What does Amazon offer?
- What is Amazon Time Sync?
- Amazon Time Sync Features
- What if Amazon Time Sync link-local service have an issue?
- What is Amazon Time Sync public NTP?
- New Update from AWS!!
- Availability
- How to configure Amazon Time Sync Public NTP for Microsoft Windows
- Conclusion
- Reference
Introduction
 Photo by Djim Loic on Unsplash
Photo by Djim Loic on Unsplash
A consistent and accurate time reference is critical to many server operations and processes. Most system logs contain timestamps that can be used to determine when the problem occurred and the order in which the events occurred.
What will happen if time is not set correctly?
 Photo by Luke Chesser on Unsplash
Photo by Luke Chesser on Unsplash
When your organization makes a request using the AWS CLI or AWS SDKs, these tools sign the request on your behalf. If the instance date and time are not set correctly, the signature date may not match the request date, and AWS will reject the request.
What does Amazon offer?

Amazon offers Amazon Time Sync, which can be accessed from any EC2 instance and can also be used by other AWS services.
The service provides accurate measurements of the current time according to the global Universal Coordinated Time standard, coordinated via the Network Time Protocol using a set of satellite links and atomic reference clocks in each AWS region. Amazon Time Sync automatically relaxes the leap seconds added to UTC.
What is Amazon Time Sync?
Amazon Time Sync is available via NTP at the IPv4 address 169.254.169.123 or fd00:ec2::123 IPv6 for all instances running in the VPC.
Amazon Time Sync Features
- Your instance does not require Internet access, and you do not need to configure security group rules or network ACLs to allow access.
- Amazon Linux 2, newer versions of Amazon Linux AMIs, and AWS Windows AMIs sync with Amazon Time Sync by default.
What if Amazon Time Sync link-local service have an issue?
You can use the Amazon Time Sync public NTP pool at time.aws.com to back up the local Amazon Time Sync link service and connect resources outside of Amazon EC2 to the Amazon Time Sync service.
What is Amazon Time Sync public NTP?
- The Amazon Time Sync public NTP automatically mitigates leap seconds added to the UTC service, just like the Amazon Time Sync service.
- The public NTP Amazon Time Sync Service is supported by satellites in AWS and a set of atomic reference clocks around the world connected to each AWS region.
New Update from AWS!!
Amazon Time Sync is now available online. Built on Amazon's network infrastructure, Amazon Time Sync uses a global set of redundant atomic and satellite-linked reference clocks in AWS regions to provide current time measurements according to the Global Coordinated Universal Time standard.
- Amazon Time Sync was previously available through EC2 instances.
- In addition to connecting directly to EC2 instances, you can now access Amazon Time Sync from time.aws.com as a public NTP service.
- This means that devices and infrastructure outside of AWS, such as IoT devices and on-premises infrastructure, can synchronize with the same high-availability time resources previously only available in AWS data centers.
Availability
Amazon Time Sync NTP pools are available globally in all public AWS regions, AWS GovCloud (US) regions, and over the Internet.
How to configure Amazon Time Sync Public NTP for Microsoft Windows
- Open Control Panel.
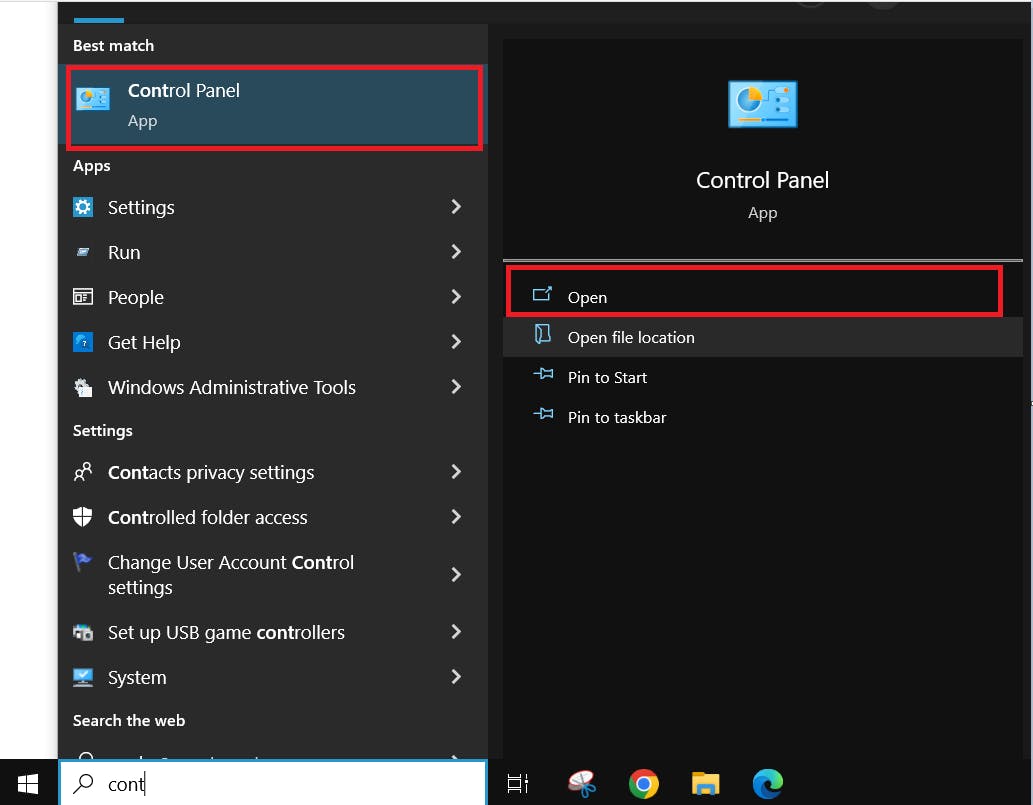
- Select the Date and Time icon.
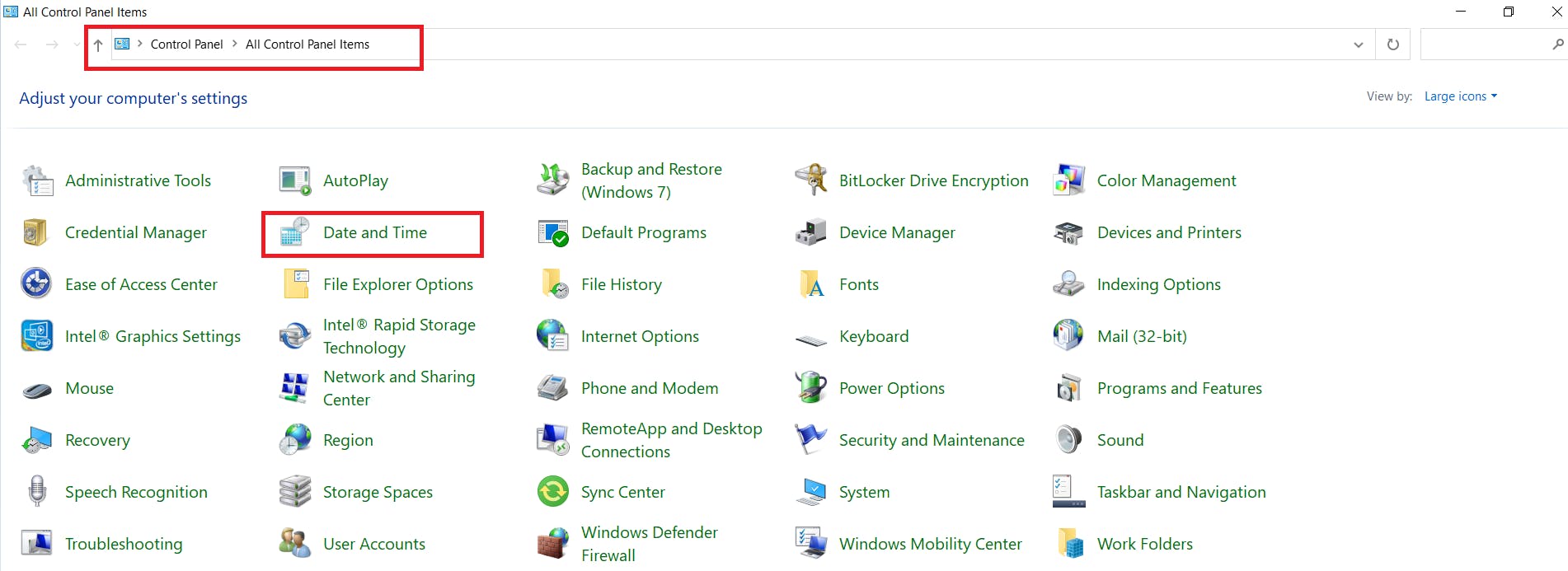
- Select the Internet Time.
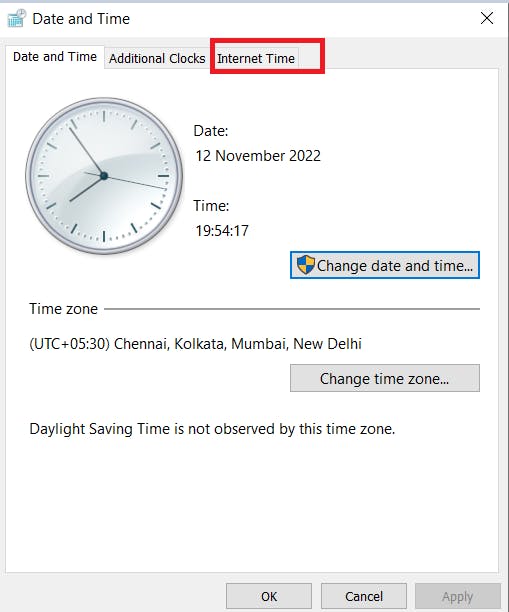
- Choose Change settings.
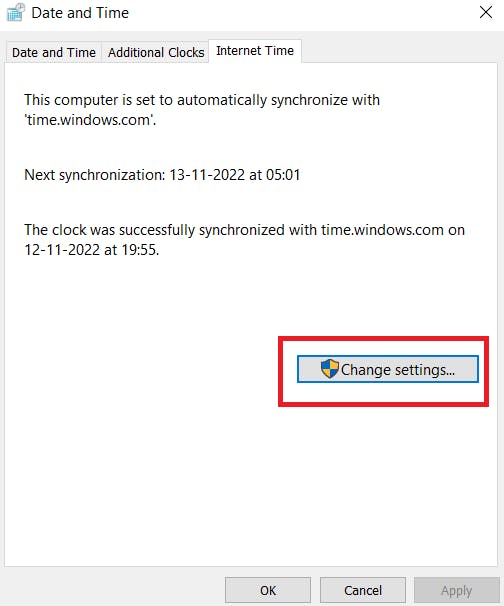
- Select the check box to synchronize with an Internet time server. Next to Server, enter time.aws.com.
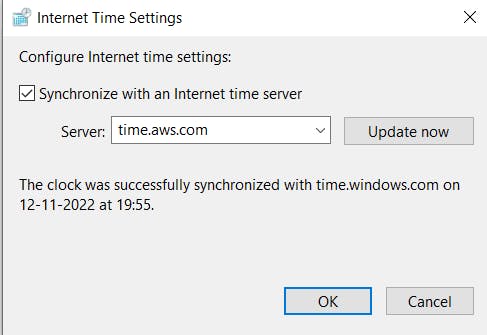
- Select Update Now.
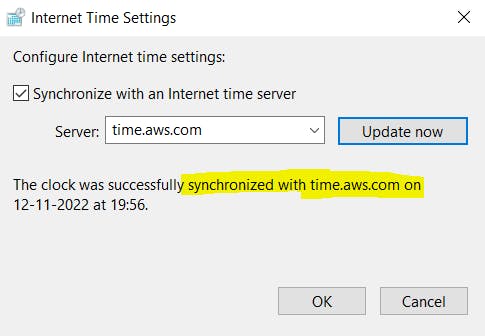
NOTE
Cannot be used if the computer is part of a domain. In this case, it synchronizes the time with the domain controller. Controllers can be configured to use Amazon Time Sync Public NTP.
Kindly watch the below video to know about the Amazon Time Sync public NTP.
Conclusion
Successfully configured the Amazon Time Sync Public NTP for Microsoft Windows.
